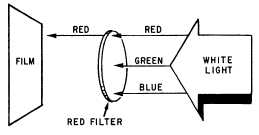
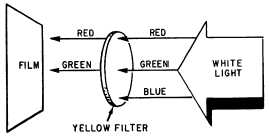
Figure 11-18.—Characteristics of a red photographic filter.
Figure 11-19.—Characteristics of a yellow photographic filter.
a yellow filter passes read and green and absorbs blue
(fig. 11-18).
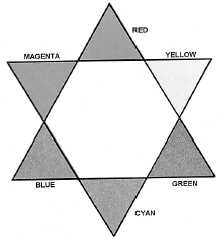
In selecting a filter in black and white
photography, you can use the color star in figure 11-19
to determine the effect of the filter on the gray scale of
the negative and the final print. On the final print, the
result will be that a filter will lighten its own color and
the colors adjacent to it and darken its complement and
the colors adjacent to its complement; for example, a
green filter will lighten green (its own color) and cyan
and yellow (adjacent colors). It will darken magenta (its
Figure 11-19.—Color star
complement) and blue and red (adjacent colors of the
complement).
FILTER DESIGNATIONS
Some filters are designated by a descriptive
name, such as neutral density, haze, polarizing and
skylight. Color compensating and color print filters have
yet another designation system.
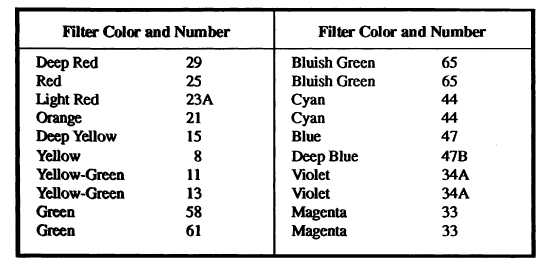
The Kodak Wratten filter line uses a
numbering system to designate its black-and-white
filters, as shown in table 11-1 that filters in the
Table 11-1.—Kodak Wratten Filter
11-17