Tungsten-Halogen Lamps
Tungsten-halogen lamps have a tungsten filament
inside a quartz envelope. This type of lamp does not
blacken the inside of the envelope and operates at an
almost constant brightness and color temperature
throughout its life. Tungsten-halogen lamps for
photography operate at color temperatures of 3200 K
and 3400 K. Filters can be used to convert them to
daylight. For its size, a tungsten-halogen lamp generally
delivers more light than a conventional 3200 K lamp.
Tungsten-halogen lights are becoming more popular
and are rapidly replacing regular tungsten lights for
general photographic use.
Fluorescent Lamps
Pictures made on daylight type of color films under
fluorescent lights without a filter may be acceptable;
however, they usually have a greenish cast. When a
tungsten type of color film is used with a fluorescent
lamp without a filter, the pictures usually are too blue.
Fluorescent light is not generated by heat, as are
other types of light. It has special characteristics
different from either daylight or tungsten light.
Fluorescent lights have no true color temperature, but a
value of approximate color temperature has been
worked out.
Daylight fluorescent lamps: 6500 K
Cool, white fluorescent lamps: 4500 K
Warm, white fluorescent lamps: 3500 K
Electronic Flash Lamps
Electronic flash is an excellent light source for both
outdoor and indoor photography, especially when the
predominant lights are fluorescent. Electronic flash uses
a discharge tube filled with xenon gas and is supplied
with a powerful charge of electricity from a capacitor.
The flash is triggered by means of an electrical current
that ionizes the gas. The output, or intensity of the flash,
is usually given in effective candlepower-seconds and
depends on the voltage and size of the capacitor. The
design of the reflector on an electronic flash has a direct
relationship on the efficiency of the unit.
Electronic flash resembles daylight in color quality
and is excellent for exposing daylight type of color
films. The duration of the flash is short, usually 1/500
second or less. With a computerized (automatic) unit
used close to the subject, the flash duration can be as
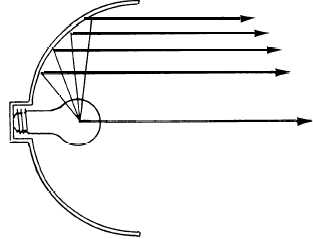
Figure 1-13.–A lamp reflector can increase the intensity of light
reaching the subject.
short as 1/50,000 second. Computerized electronic flash
units have a sensor that switches off the flash when the
subject (depending on its distance and tone) has received
enough light for proper exposure.
Reflectors
Two types of reflectors are of importance in
photography. They are the lamp reflector and the plane
reflector. The first type, the lamp reflector, is used with
artificial light sources-tungsten, tungsten-halogen,
fluorescent, and electronic flash lamps to direct the light.
The second type, the plane reflector, is used to redirect
light from any kind of light source into shaded areas to
soften or lighten shadows. (While it is true that mirrors
are also reflectors, reflector is used in photography as a
more general term. Mirrors always reflect specular light;
and reflectors reflect either specular or diffused light.)
LAMP REFLECTORS. –Light emitted by the
filament of a lamp is dispersed in all directions. This is
useful when the lamp is for general illumination, such
as one suspended from the ceiling to light a room. As a
photographer, however, you are usually interested in
illuminating only a given area, and it is, therefore, to
your advantage to concentrate the light emitted by a
lamp onto the area of interest. You can do this by
mounting the lamp in a concave reflector that reflects
almost all the light onto the area to be photographed
(fig. 1-13). Lamp reflectors generally have a satin or
matte finish to diffuse the reflected light to prevent hot
spots that could result if the reflector surface were highly
polished.
Reflectors of electronic flash units vary con-
siderably in their efficiency and covering power at
1-9